The Intel Xeon series based on the Netburst microarchitecture is a family of x86 compatible microprocessors designed for server and workstations.
With the Netburst Xeon, Intel introduced the suffixes DP and MP. DP stands for dual-processoring, MP stands for multi-processoring.
Intel Xeon Foster
In mid-2001, the Xeon brand was introduced ("Pentium" was dropped from the name). The initial variant that used the new NetBurst microarchitecture, "Foster", was slightly different from the desktop Pentium 4 ("Willamette"). It was a decent chip for workstations, but for server applications it was almost always outperformed by the older Cascades cores with a 2 MB L2 cache and AMD's Athlon MP. Combined with the need to use expensive Rambus Dynamic RAM, the Foster's sales were somewhat unimpressive.
Intel Xeon 1.7 GHz
Kindly donated by Pauli Rautakorpi.
|
1.7 GHz Specification Details |
Show | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Xeon Prestonia
In 2002 Intel released a 130 nm version of Xeon branded CPU, codenamed "Prestonia". It supported Intel's new Hyper-Threading technology and had a 512 kB L2 cache. This was based on the "Northwood" Pentium 4 core. The Prestonia performed much better than its predecessor and noticeably better than Athlon MP. The support of new features in the E75xx series also gave it a key advantage over the Pentium III Xeon and Athlon MP branded CPUs (both stuck with rather old chipsets), and it quickly became the top-selling server/workstation processor.
Intel Xeon 1.8 GHz
|
1.8 GHz Specification Details |
Show | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Intel Xeon 2 GHz
Kindly donated by Pauli Rautakorpi.
|
2 GHz Specification Details |
Show | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Intel Xeon 2.2 GHz
|
2.2 GHz Specification Details |
Show | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Intel Xeon 2.4 GHz
|
2.4 GHz Specification Details |
Show | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
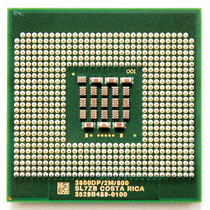
Intel Xeon 2.8 GHz
Kindly donated by Pauli Rautakorpi.
|
2.8 GHz Specification Details |
Show | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Xeon Nocona
Due to a lack of success with Intel's Itanium and Itanium 2 processors, AMD was able to introduce x86-64, a 64-bit extension to the x86 architecture. Intel followed suit by including Intel 64 (formerly EM64T; it is almost identical to AMD64) in the 90 nm version of the Pentium 4 ("Prescott"), and a Xeon version codenamed "Nocona" with 1 MB L2 cache was released in 2004. The Xeon was noticeably slower than AMD's Opteron, although it could be faster in situations where Hyper-Threading came into play.
Intel Xeon 2.8 GHz
|
2.8 GHz Specification Details |
Show | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Intel Xeon 3.0 GHz
|
3.0 GHz Specification Details |
Show | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Intel Xeon 3.4 GHz
|
3.4 GHz Specification Details |
Show | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Xeon Irwindale
A slightly updated core called "Irwindale" was released in early 2005, with 2 MB L2 cache and the ability to have its clock speed reduced during low processor demand. Although it was a bit more competitive than the Nocona had been, independent tests showed that AMD's Opteron still outperformed Irwindale. Both of these Prescott-derived Xeons have the product code 80546.
Intel Xeon 2.8 GHz
|
2.8 GHz Specification Details |
Show | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Intel Xeon 3 GHz
|
3 GHz Specification Details |
Show | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Intel Xeon 3.2 GHz
|
3.2 GHz Specification Details |
Show | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Intel Xeon 3.8 GHz
|
3.8 GHz Specification Details |
Show | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
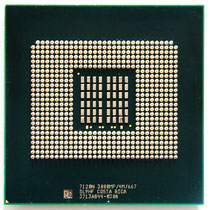
The Xeon (MP) Tulsa
Released on 29 August 2006, the 7100 series, codenamed Tulsa (product code 80550), is an improved version of Paxville MP, built on a 65 nm process, with 2 MB of L2 cache (1 MB per core) and up to 16 MB of L3 cache. It uses Socket 604.
Intel Xeon MP 7120N
|
MP 7120N Specification Details |
Show | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Not sure where to go?